I Got Me One of These - NVIDIA Jetson AGX Thor Developer Kit
I got me one of these!


This thing is a beast and I am keen to see what kind of AI robotics experiments I can create from this.
I got me one of these!


This thing is a beast and I am keen to see what kind of AI robotics experiments I can create from this.
These days I am often creating small generic re-usable building blocks that I can pontentially use across new or existing projects, in this blog I talk about the architecture for a LLM based voice chatbot in a web browser built entirely as a serverless based solution.
The key component of this solution is using Amazon Nova 2 Sonic, a speech-to-speech foundation model that can understand spoken audio directly and generate voice responses - all through a single bidirectional stream from the browser directly to Amazon Bedrock, with no backend servers required - no EC2 instances and no Containers.
This diagram illustrates the complete flow from a user speaking into their microphone to hearing the AI assistant's voice response.
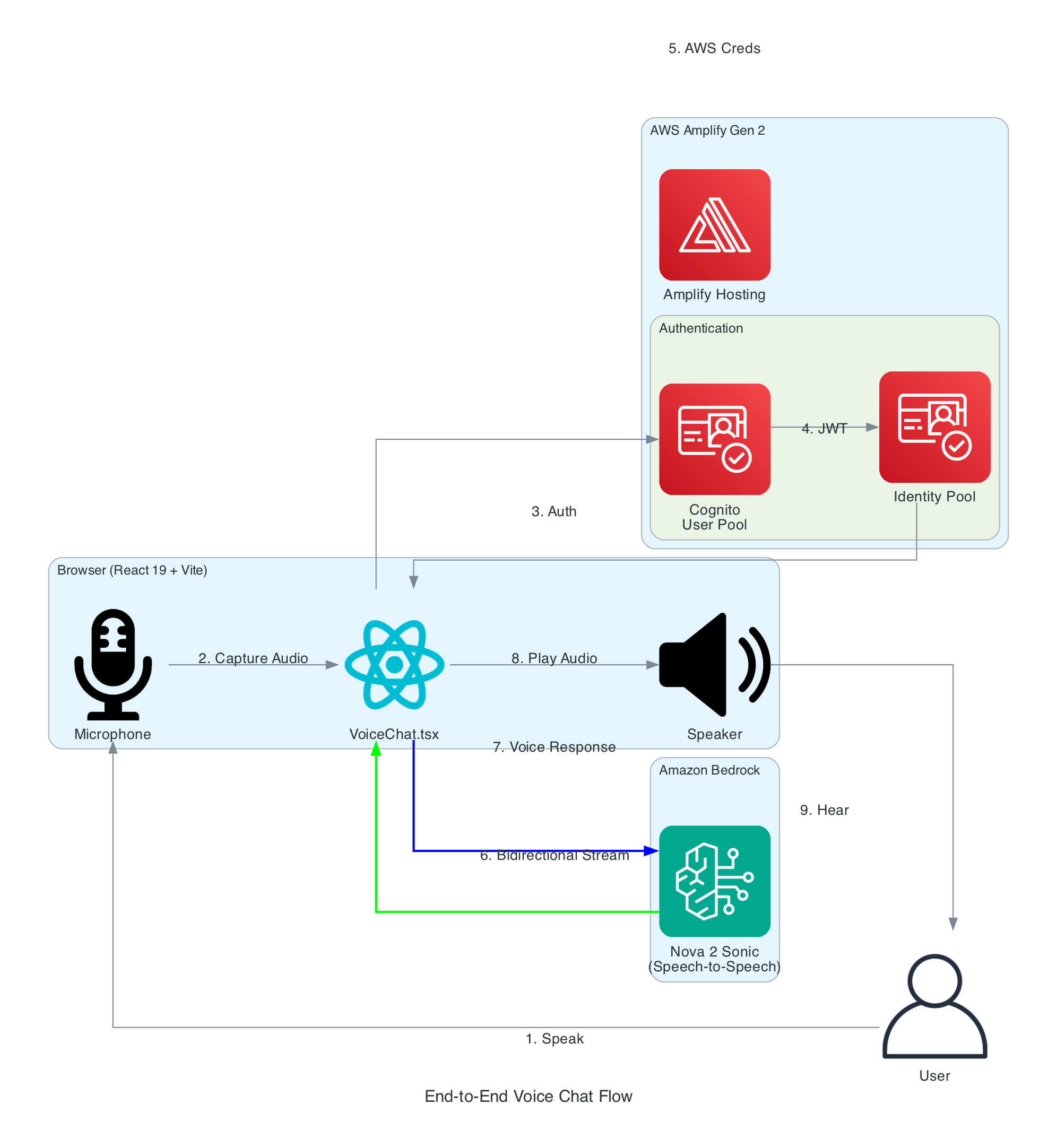
Flow Steps:
InvokeModelWithBidirectionalStreamFrom user speech to AI voice response via Amazon Nova 2 Sonic
This diagram details the internal architecture of the React application, showing how custom hooks orchestrate audio capture, Bedrock communication, and playback.
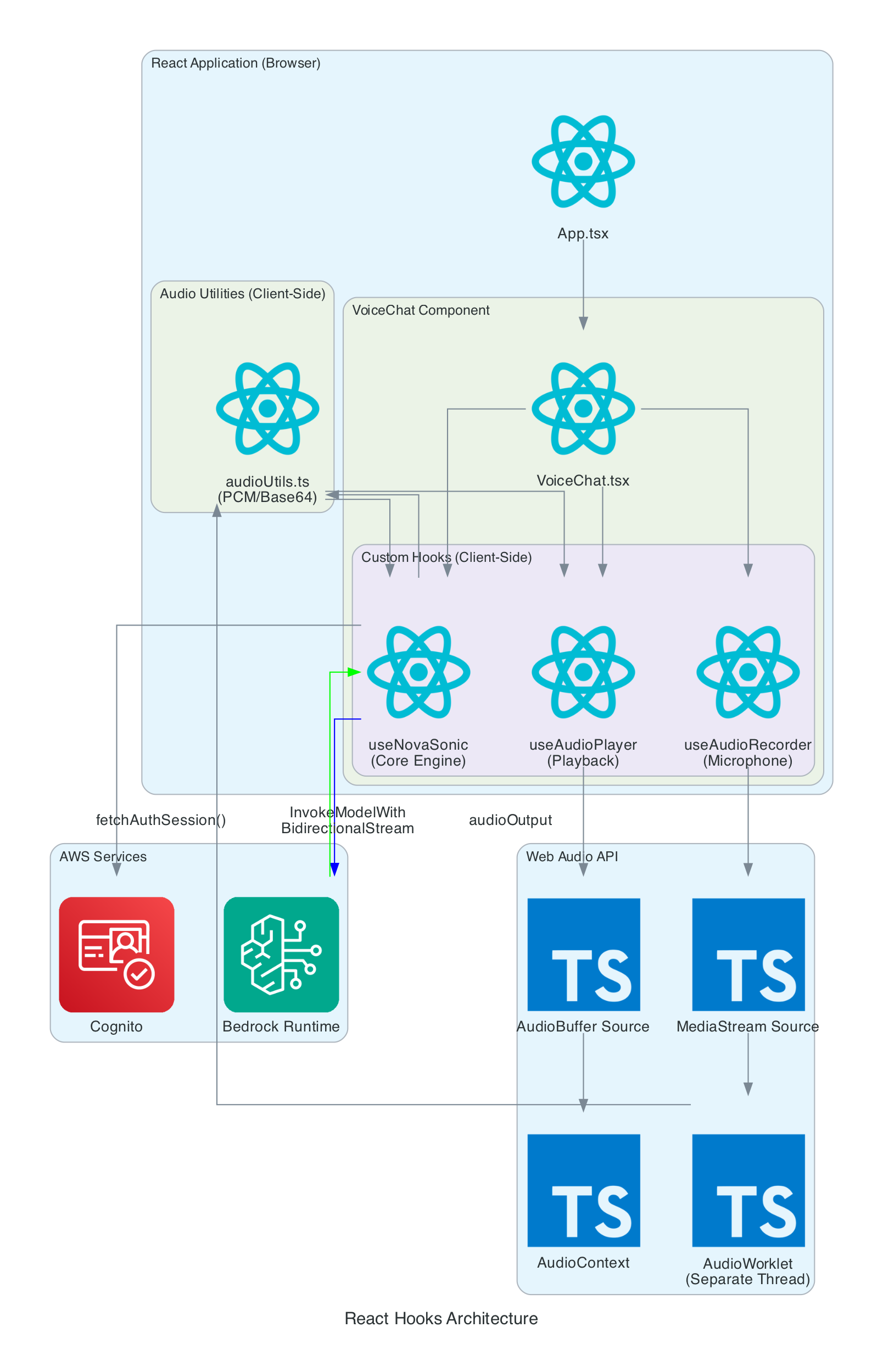
Components:
Data Flow:
useAudioRecorder via MediaStreamuseNovaSonic streams audio chunks to BedrockuseAudioPlayer queues AudioBuffers and plays through AudioContextThis diagram shows the multi-layer authentication flow that enables secure browser-to-Bedrock communication without exposing long-term credentials.
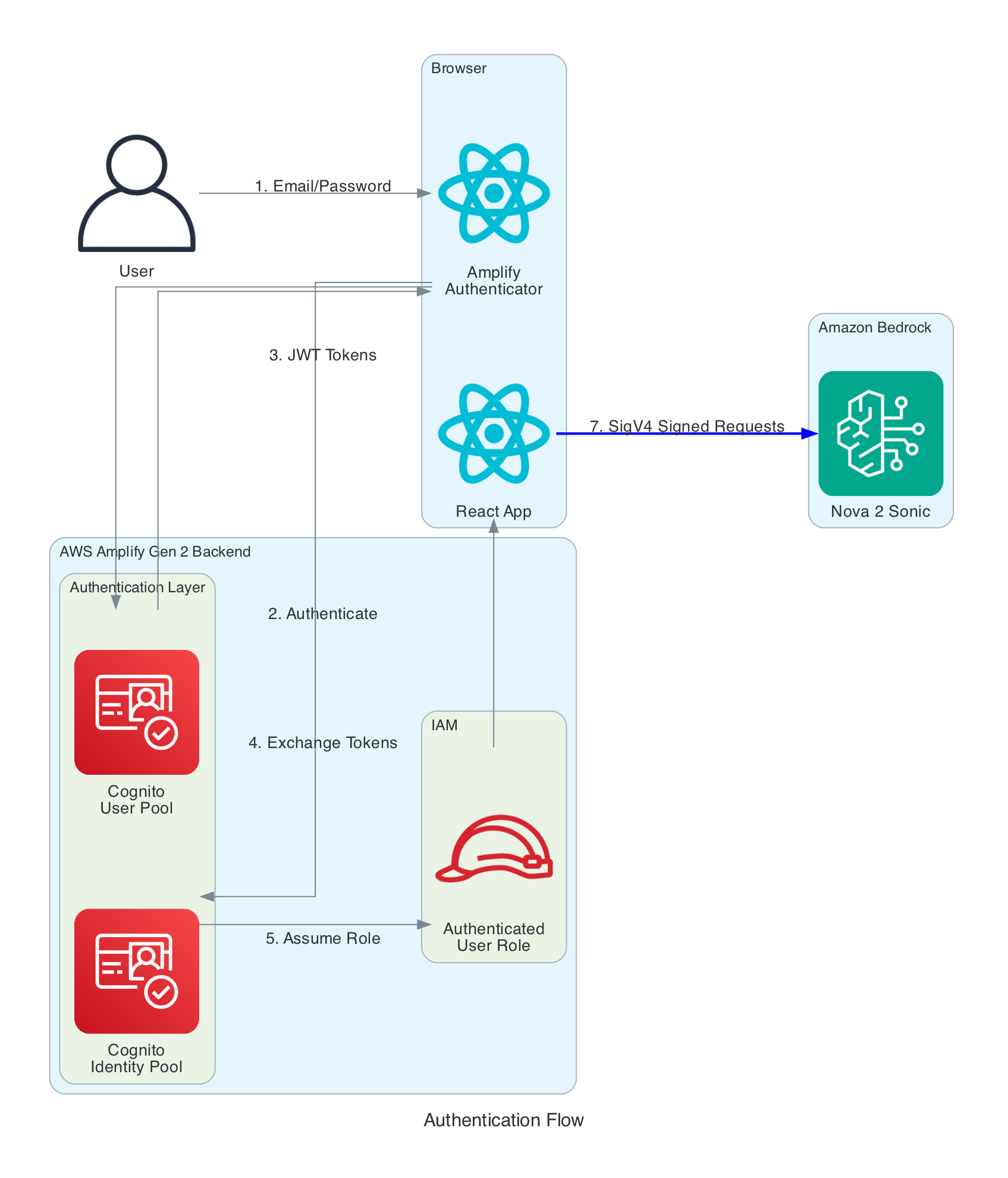
Authentication Layers:
Key Security Features:
amazon.nova-2-sonic-v1:0)This diagram shows the real-time audio processing that converts browser audio to Bedrock's required format and vice versa.
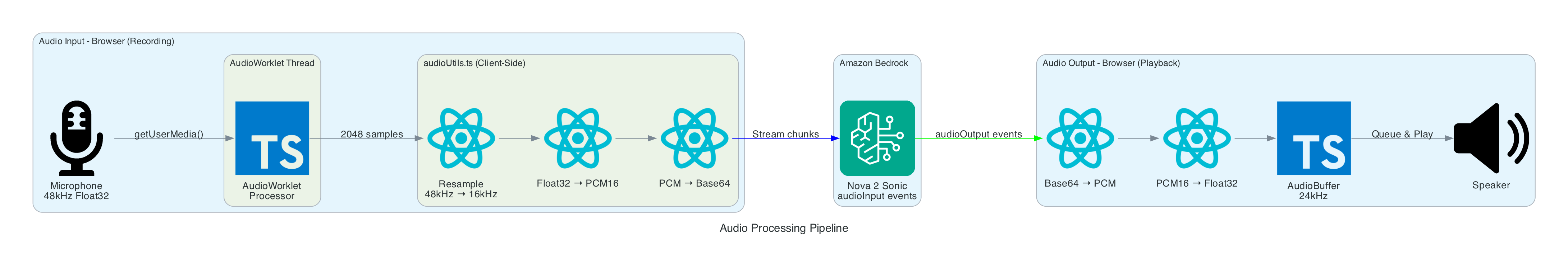
Input Processing (Recording):
Output Processing (Playback):
Real-time audio capture, format conversion, and playback
This diagram illustrates how the useNovaSonic hook manages the complex bidirectional streaming protocol with Amazon Bedrock.

Event Protocol: Nova Sonic uses an event-based protocol where each interaction consists of named sessions, prompts, and content blocks.
Input Events (sent to Bedrock):
Output Events (received from Bedrock):
Async Generator Pattern:
The SDK requires input as AsyncIterable<Uint8Array>. The hook implements this using:
This diagram provides a comprehensive view of all components - the entire solution is serverless with no EC2 instances or containers to manage.
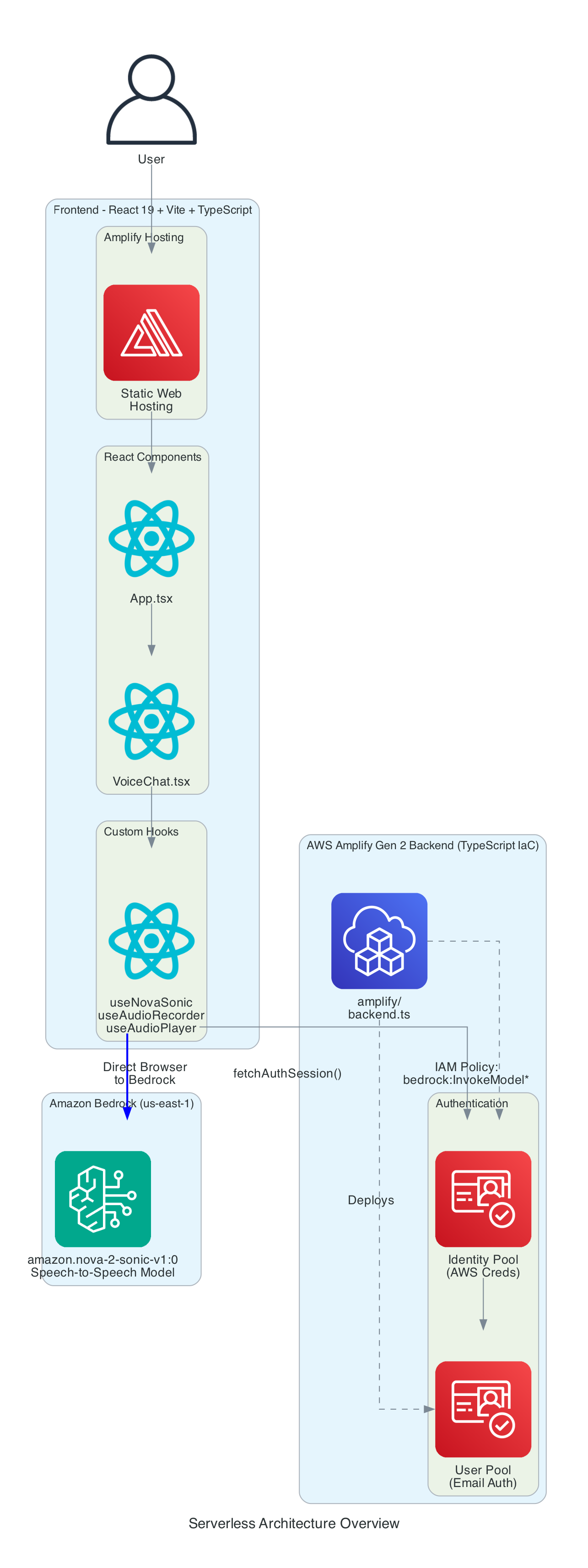
Frontend Stack:
Backend Stack (Amplify Gen 2):
bedrock:InvokeModel permission for bidirectional streamingAI Service:
Problem: Loading AudioWorklet from external file fails with CORS errors on some deployments.
Solution: Inline the AudioWorklet code as a Blob URL:
const blob = new Blob([audioWorkletCode], { type: 'application/javascript' });
const workletUrl = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
await audioContext.audioWorklet.addModule(workletUrl);
URL.revokeObjectURL(workletUrl);
Problem: Browsers capture audio at 48kHz, but Nova Sonic requires 16kHz input.
Solution: Linear interpolation resampling in real-time:
const resampleAudio = (audioData: Float32Array, sourceSampleRate: number, targetSampleRate: number) => {
const ratio = sourceSampleRate / targetSampleRate;
const newLength = Math.floor(audioData.length / ratio);
const result = new Float32Array(newLength);
for (let i = 0; i < newLength; i++) {
const srcIndex = i * ratio;
const floor = Math.floor(srcIndex);
const ceil = Math.min(floor + 1, audioData.length - 1);
const t = srcIndex - floor;
result[i] = audioData[floor] * (1 - t) + audioData[ceil] * t;
}
return result;
};
Problem: AWS SDK requires input as AsyncIterable<Uint8Array>, but events need to be pushed dynamically during the conversation.
Solution: Async generator with event queue and promise-based backpressure:
async function* createInputStream() {
while (isActiveRef.current && !ctrl.closed) {
while (ctrl.eventQueue.length > 0) {
yield ctrl.eventQueue.shift();
}
const nextEvent = await new Promise(resolve => {
ctrl.resolver = resolve;
});
if (nextEvent === null) break;
yield nextEvent;
}
}
GitHub Repository: https://github.com/chiwaichan/amplify-react-amazon-nova-2-sonic-voice-chat
Enable Nova 2 Sonic in Bedrock Console (us-east-1 region)
Clone and Install:
git clone https://github.com/chiwaichan/amplify-react-amazon-nova-2-sonic-voice-chat.git
cd amplify-react-amazon-nova-2-sonic-voice-chat
npm install
npx ampx sandbox
npm run dev
http://localhost:5173, create an account, and start talking!This architecture provides a reusable building block for voice-enabled AI applications:
The entire interaction happens in real-time: speak naturally, and hear the AI respond within seconds.
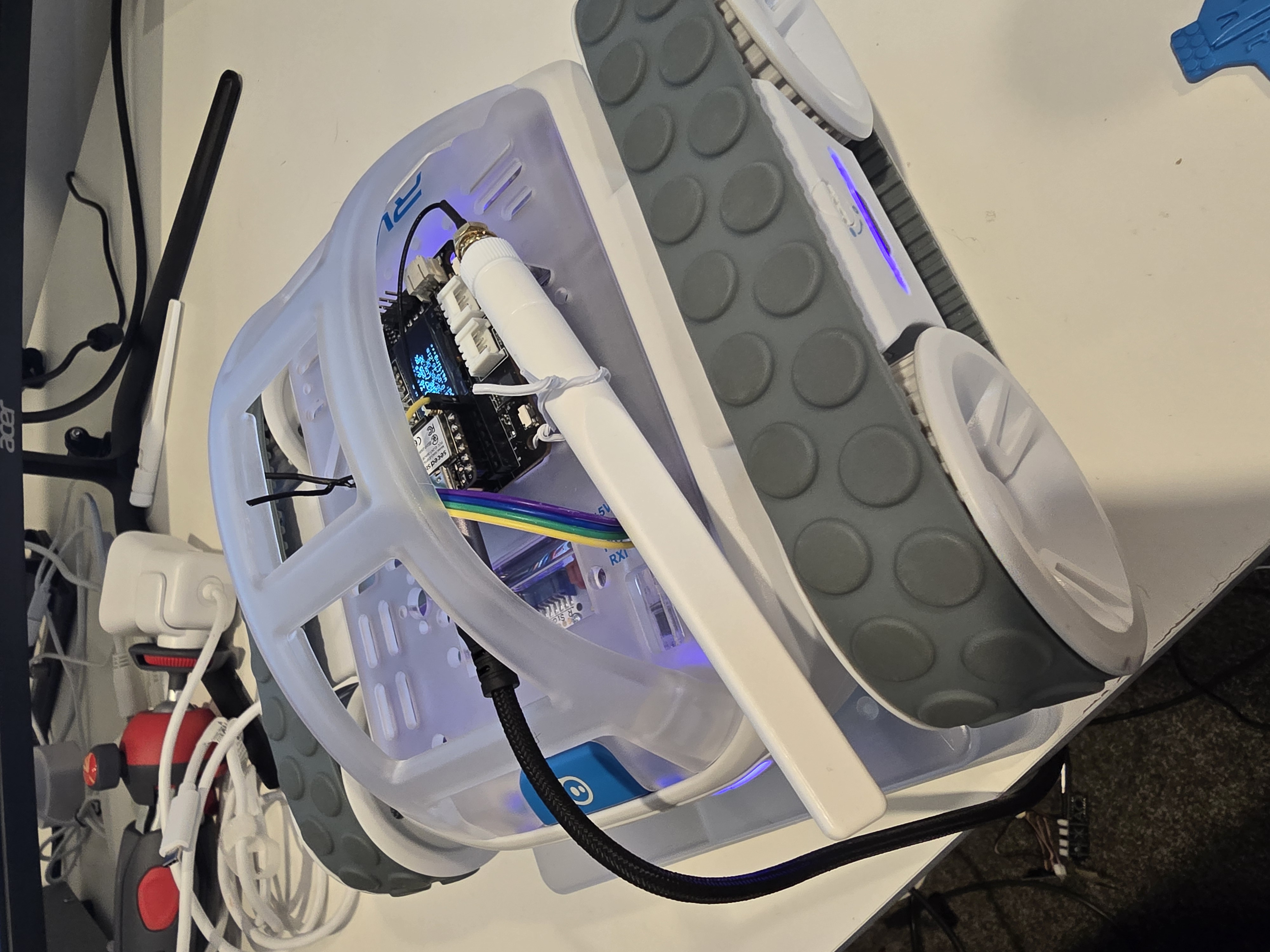
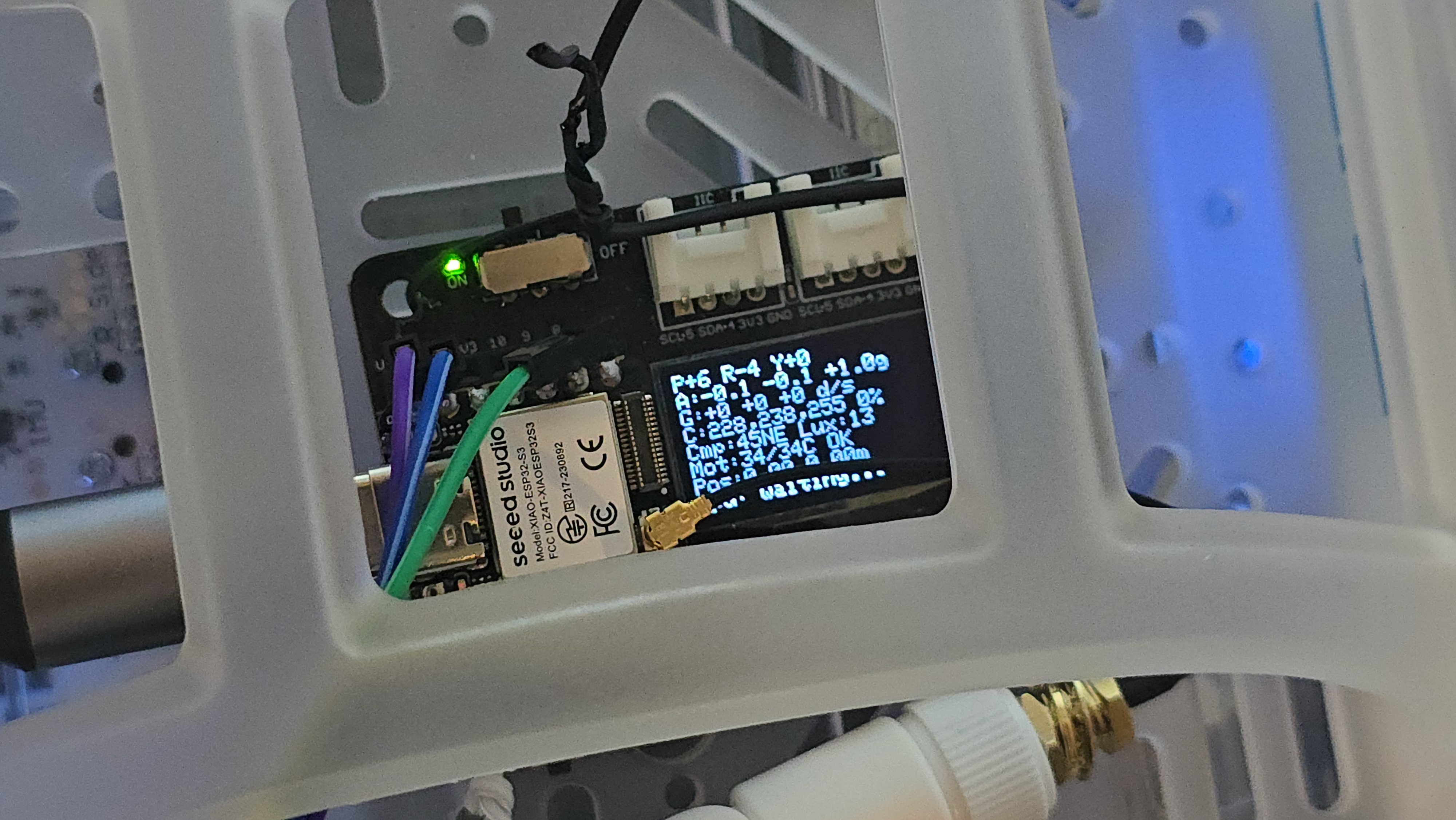

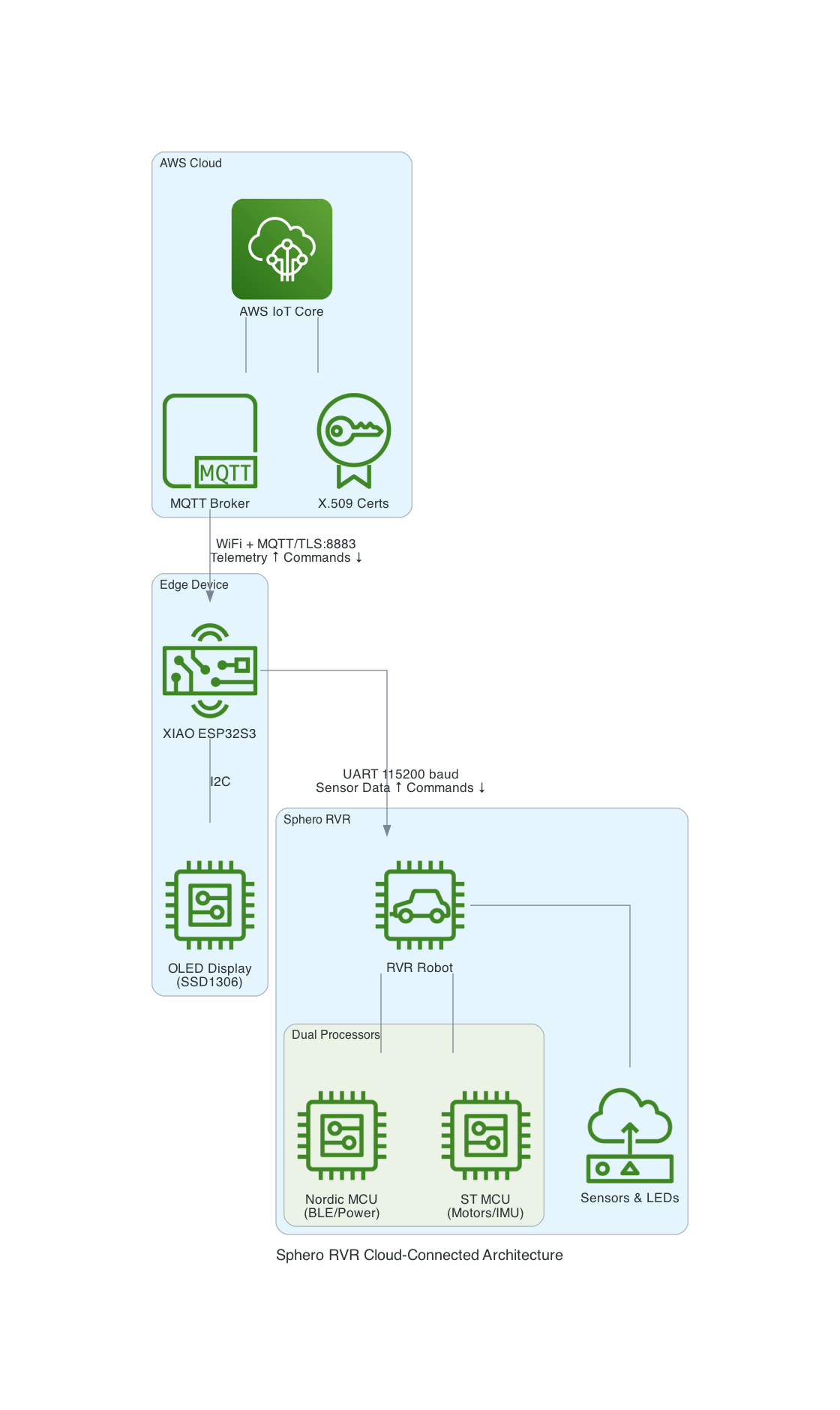
A Sphero RVR integrated with a Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32S3 with telemetry uploaded into, and also, basic drive remote control commands received from any where leveraging AWS IoT Core.
Lately I have been aiming to go deep on AI Robotics, and last year I have been slowly experimenting more and more with anything that is AI, IoT and Robotics related; with the intention of learning and going as wide and as deep as possible in any pillars I can think of. You can check out my blogs under the Robotics](/projects/robotics) Project to see what I have been up to. This year I want to focus on enabling mobility for my experiments - as in providing wheels for solutions to move around the house, ideally autonomously; starting off with wheel based solutions bought off-shelve, followed by solutions that I build myself from open-sourced projects people have kindly contirbuted online, and then ambitiously designed, 3D Printed and built all from the ground up - perhaps in a couple of years time.
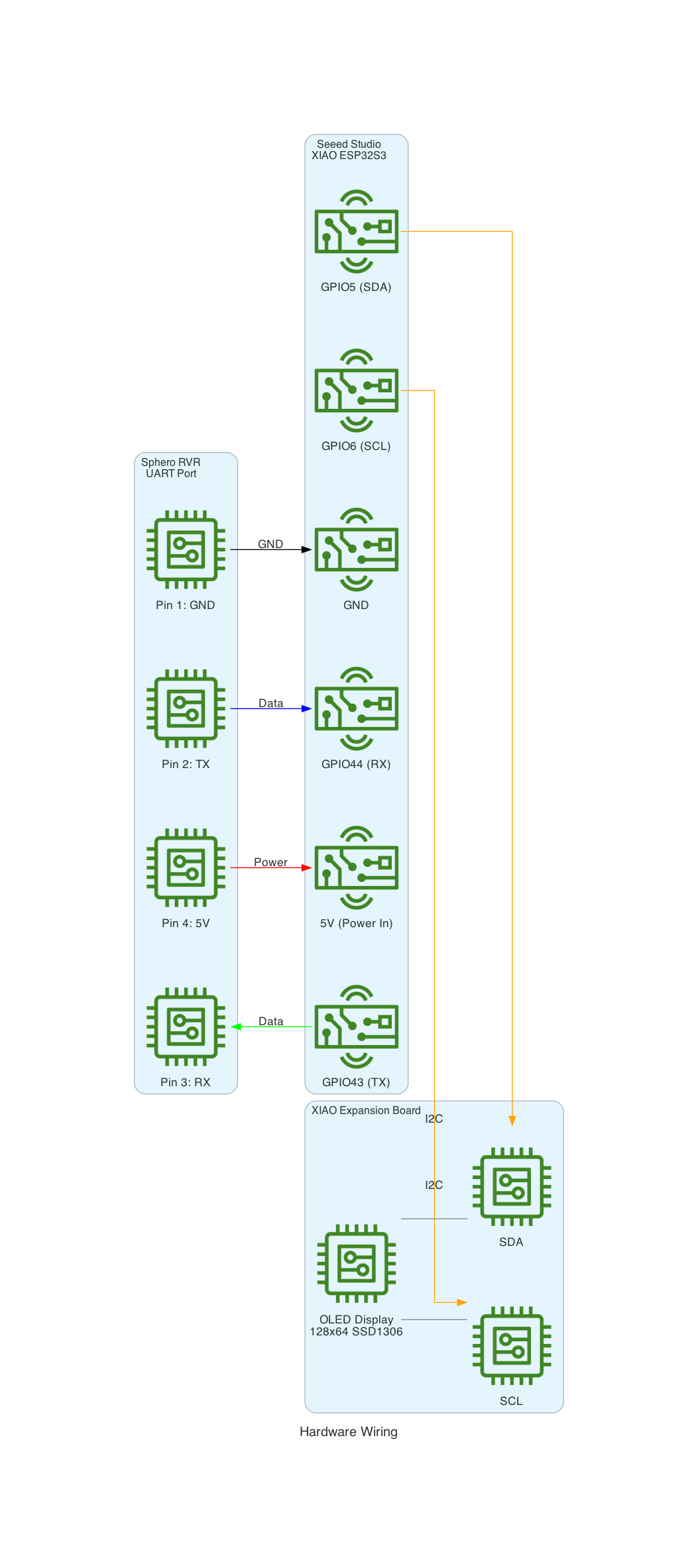
This project uses a Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32S3 microcontroller to communicate with a Sphero RVR robot via UART, while simultaneously connecting to AWS IoT Core over WiFi. The system publishes real-time sensor telemetry and accepts remote drive commands through MQTT.
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32S3 | Compact ESP32-S3 microcontroller with WiFi, 8MB flash |
| Sphero RVR | Programmable robot with motors, IMU, color sensor, encoders |
| XIAO Expansion Board | Provides OLED display (128x64 SSD1306) for status info |
The system publishes comprehensive sensor data every 60 seconds:
Control the RVR from anywhere using JSON commands:
The XIAO Expansion Board's OLED display shows real-time sensor readings for local monitoring.
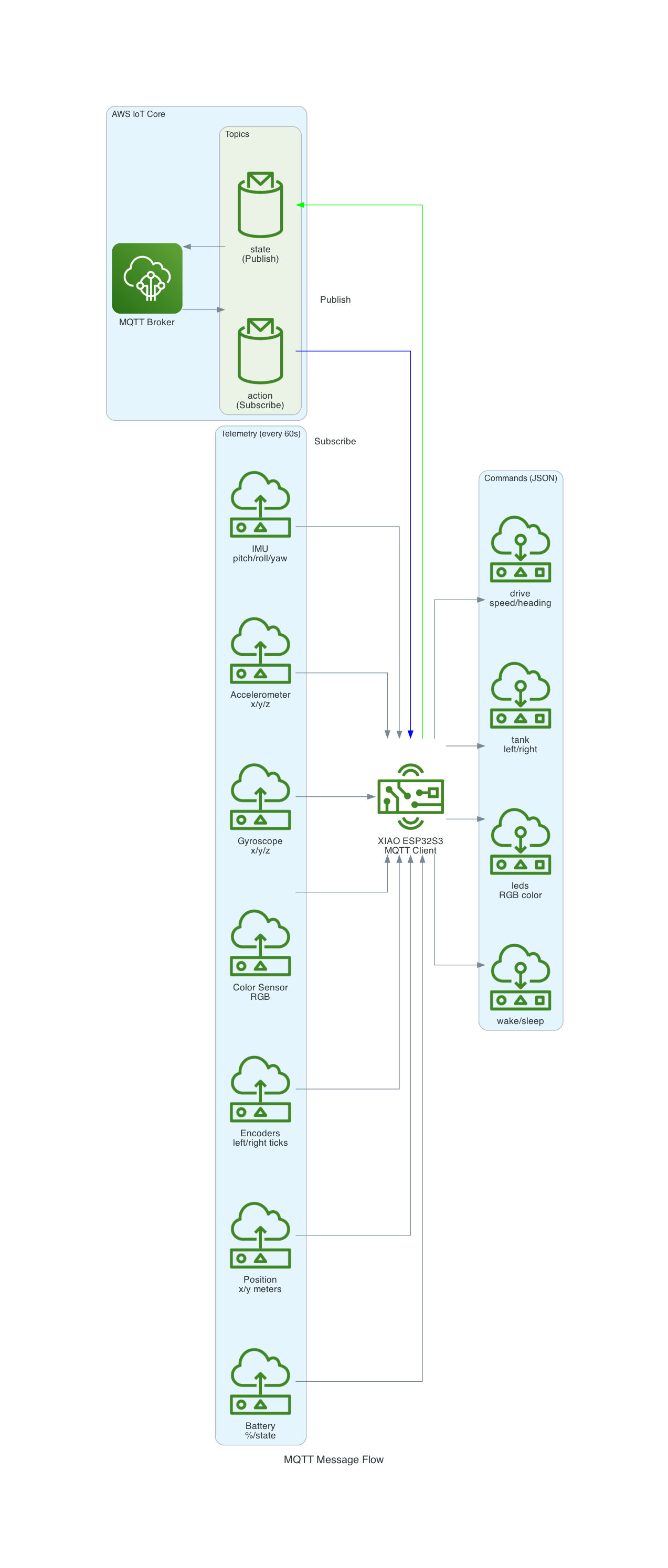
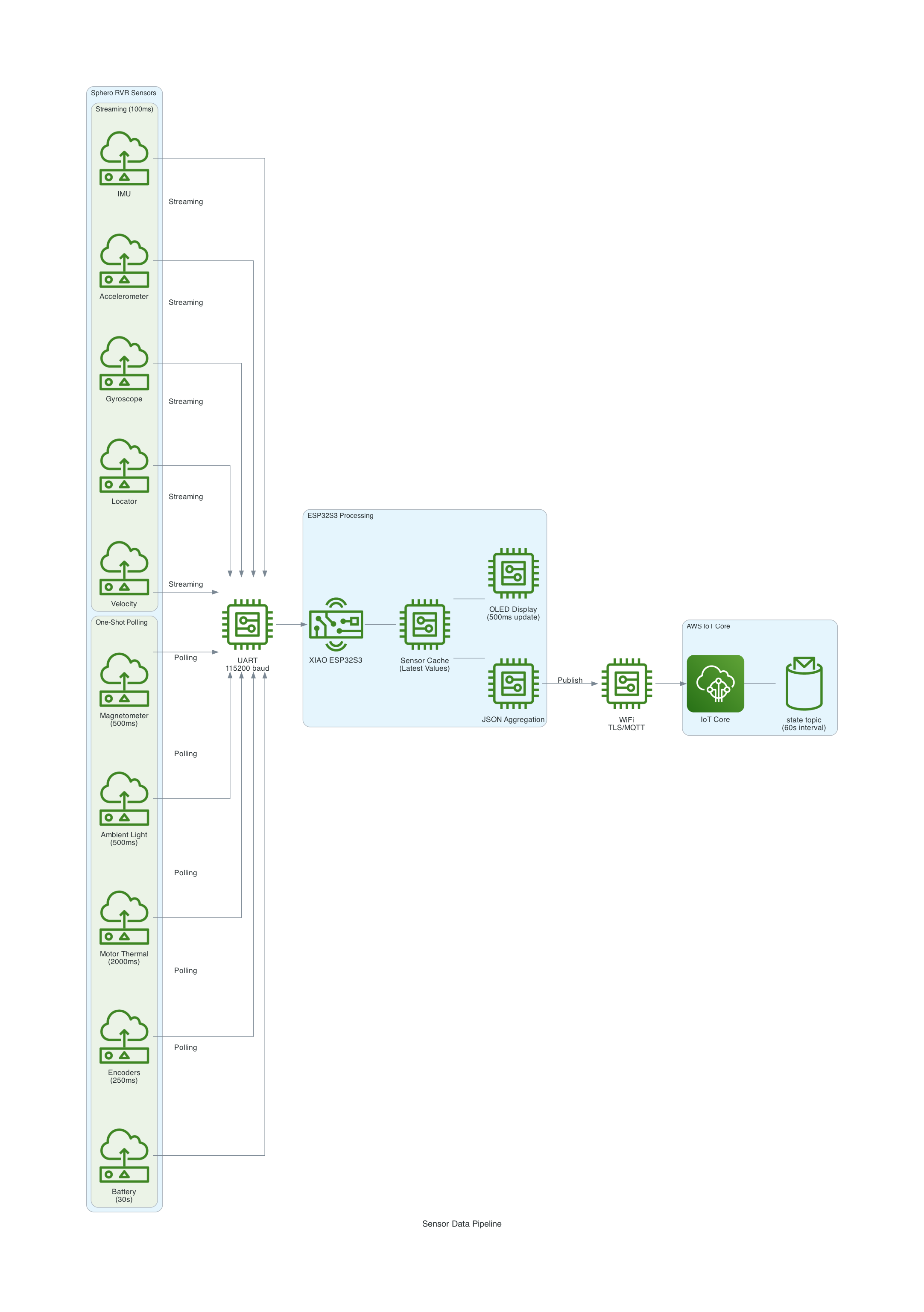
The XIAO ESP32S3 acts as a bridge between the Sphero RVR and AWS IoT Core:
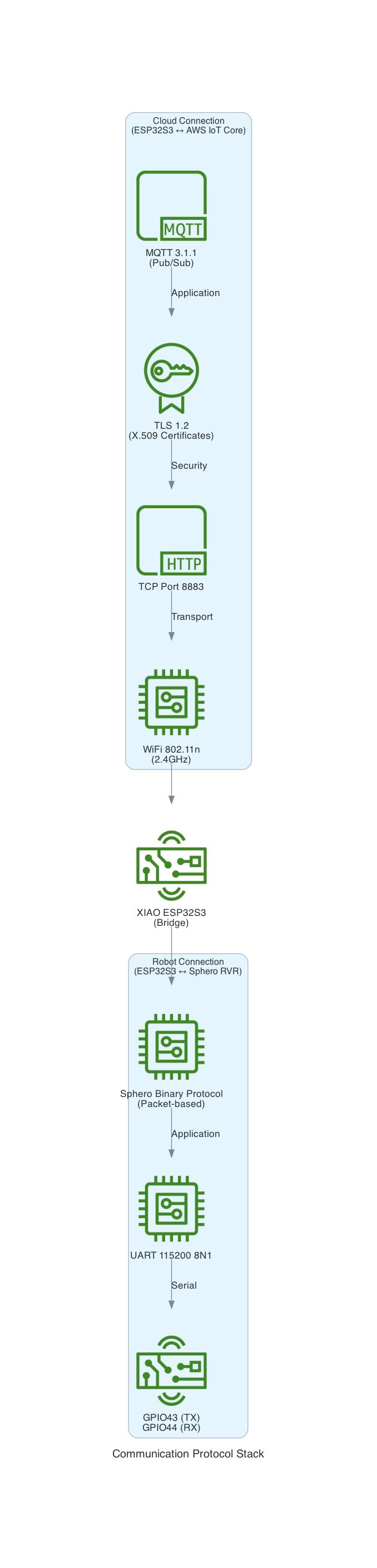
The Sphero RVR uses a binary packet-based protocol over UART. Each packet contains a start-of-packet byte (0x8D), an 8-byte header with device ID and command ID, variable-length data body, checksum, and end-of-packet byte (0xD8). The RVR has two internal processors: Nordic (handles BLE, power, color detection) and ST (handles motors, IMU, encoders).
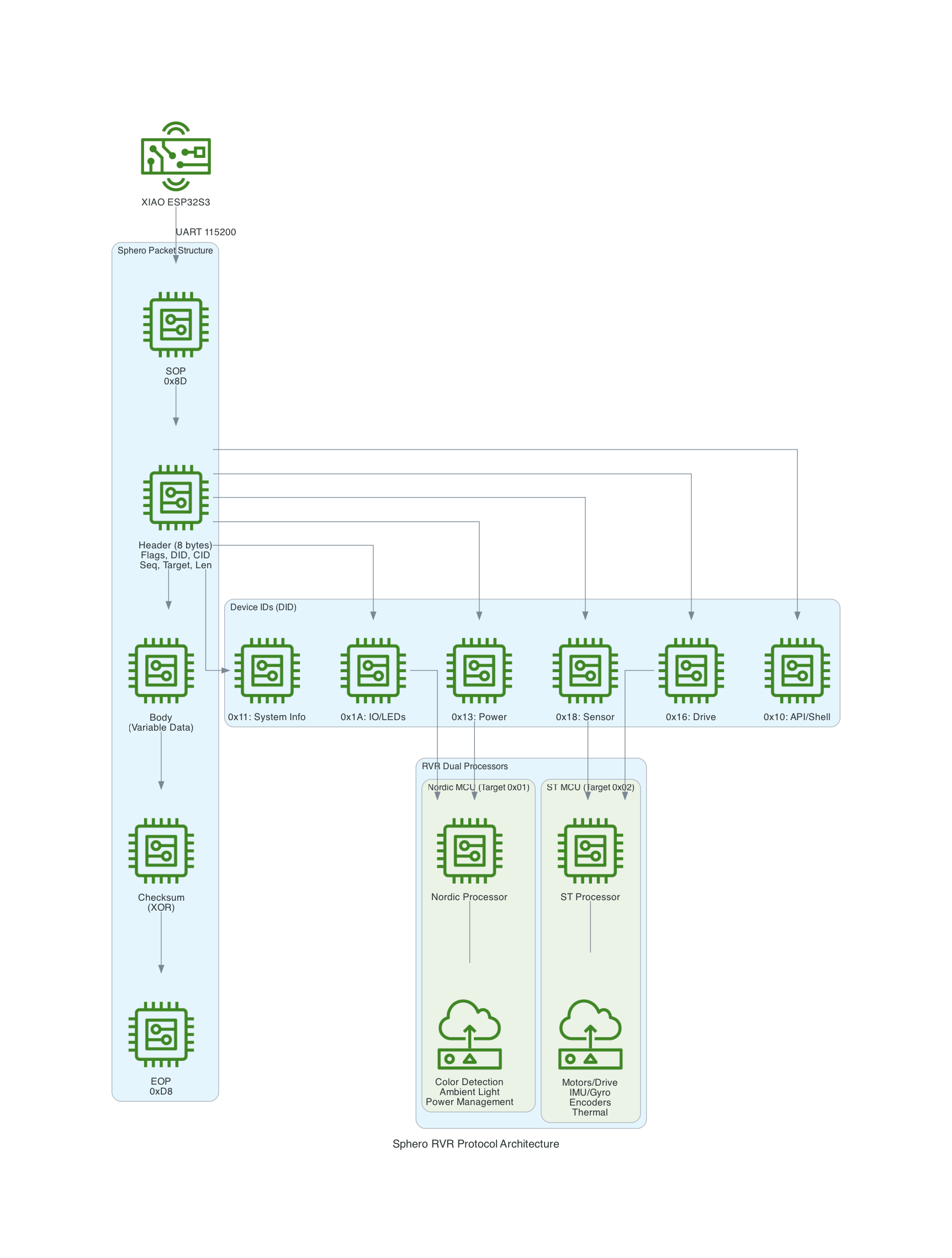
I ported the code into this project to control the RVR using the UART protocol based on the Sphero SDK.
You can find the source code for this project here: https://github.com/chiwaichan/platformio-aws-iot-seeed-studio-esp32s3-sphero-rvr



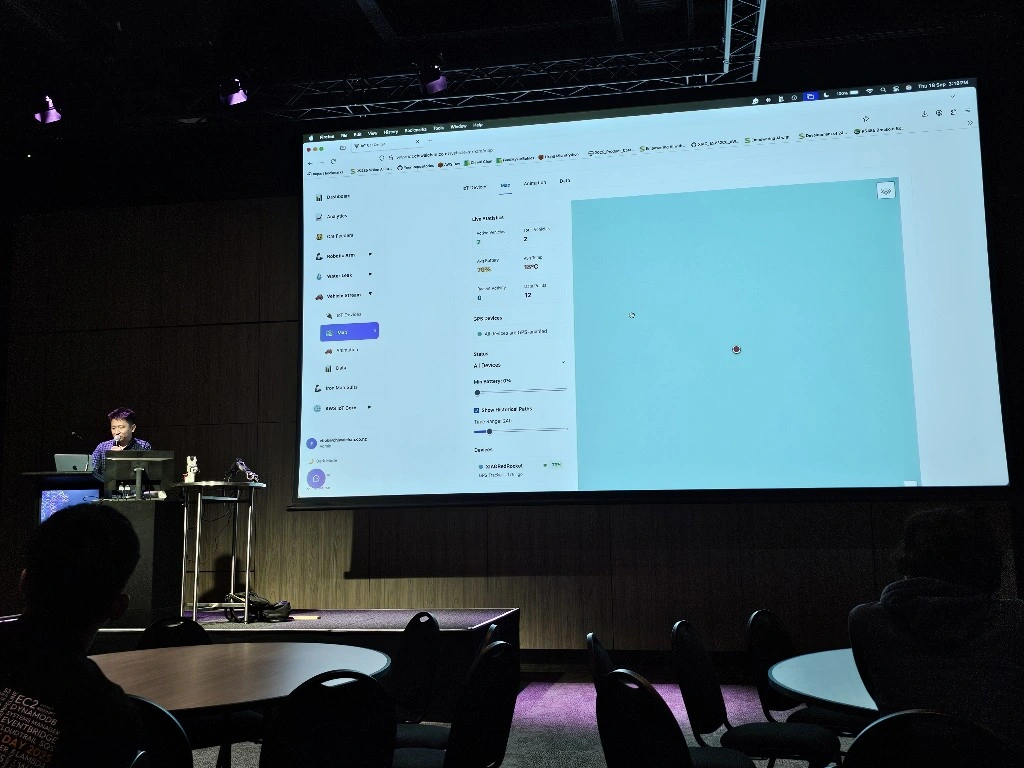
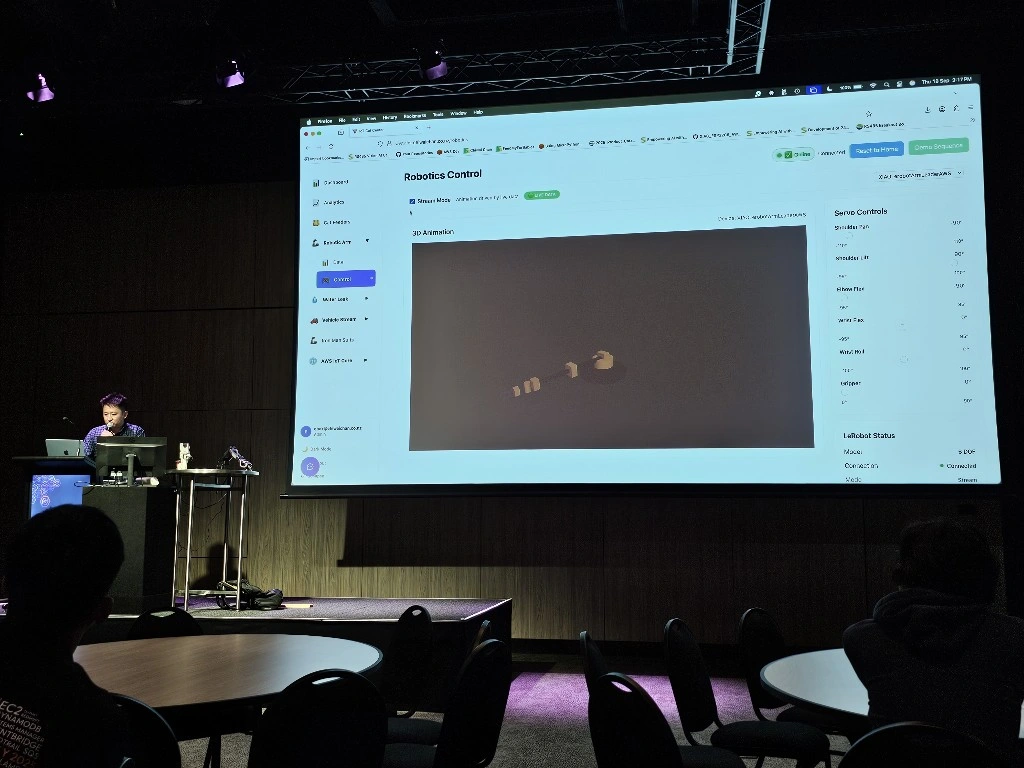
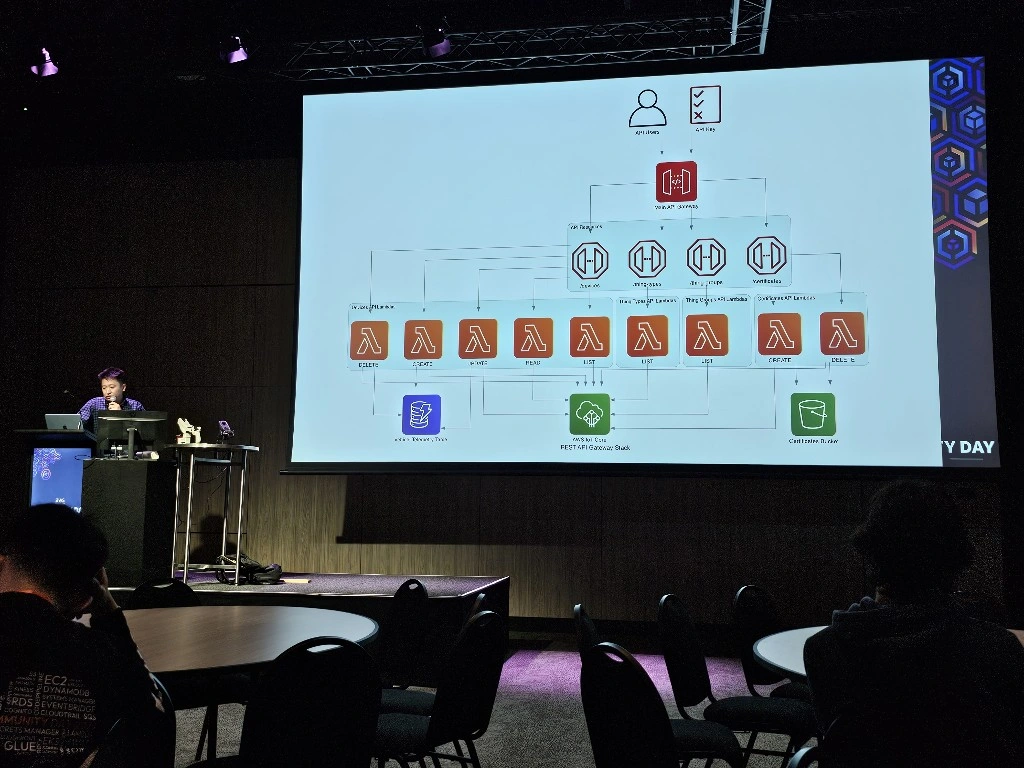
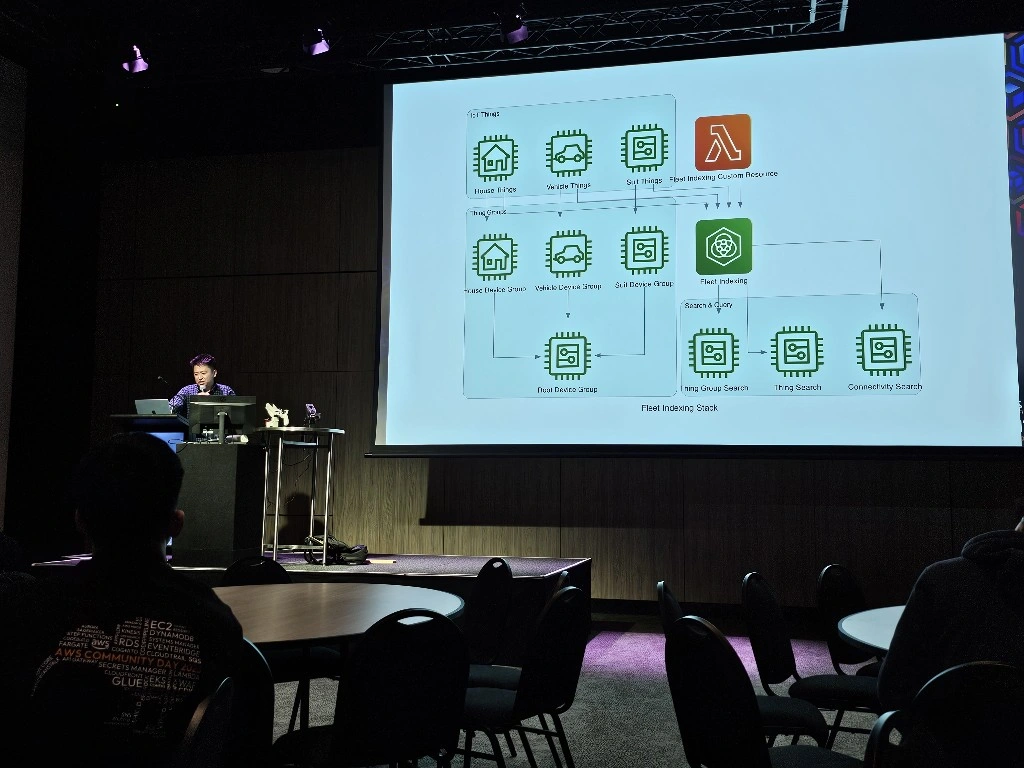
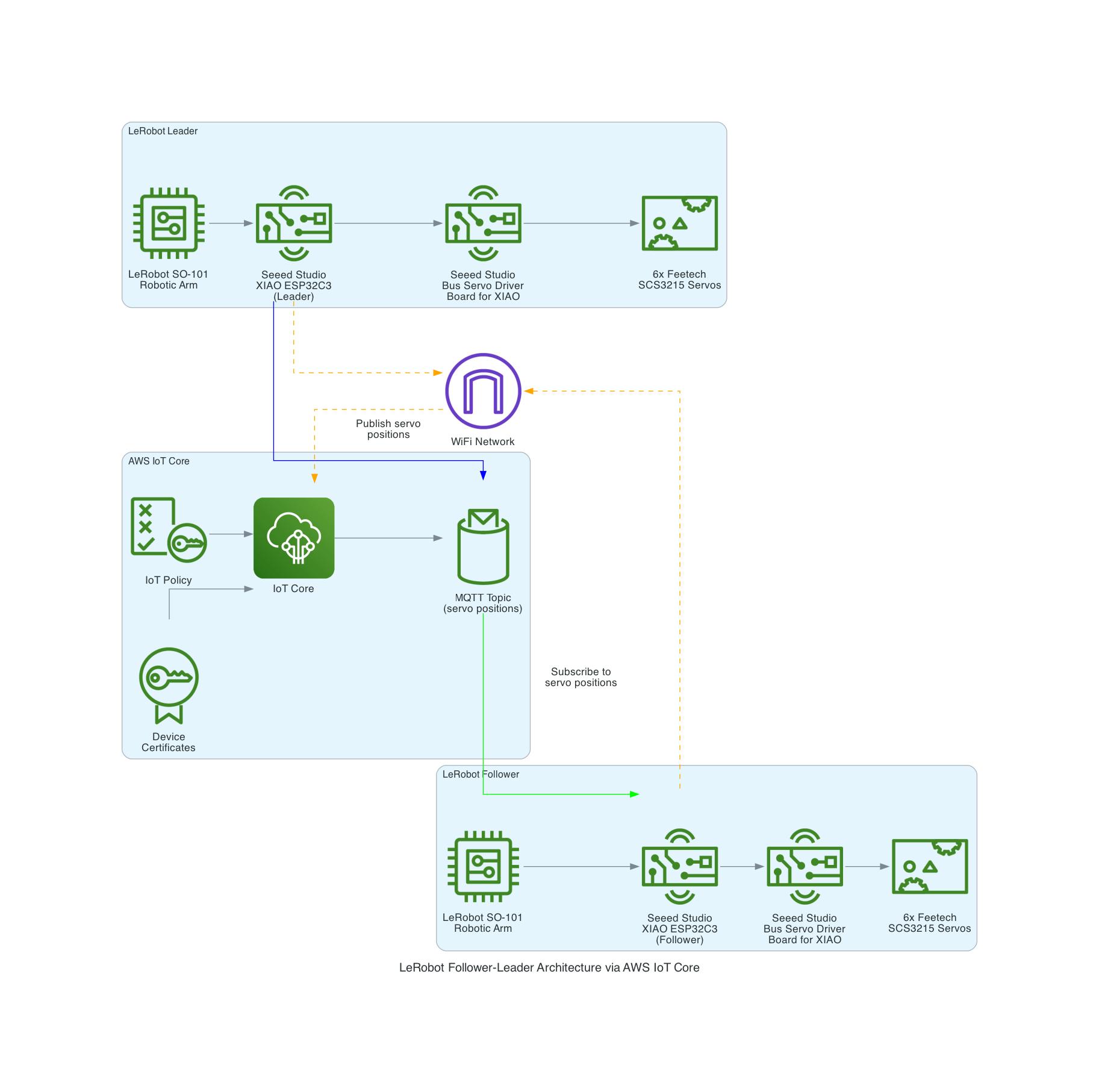
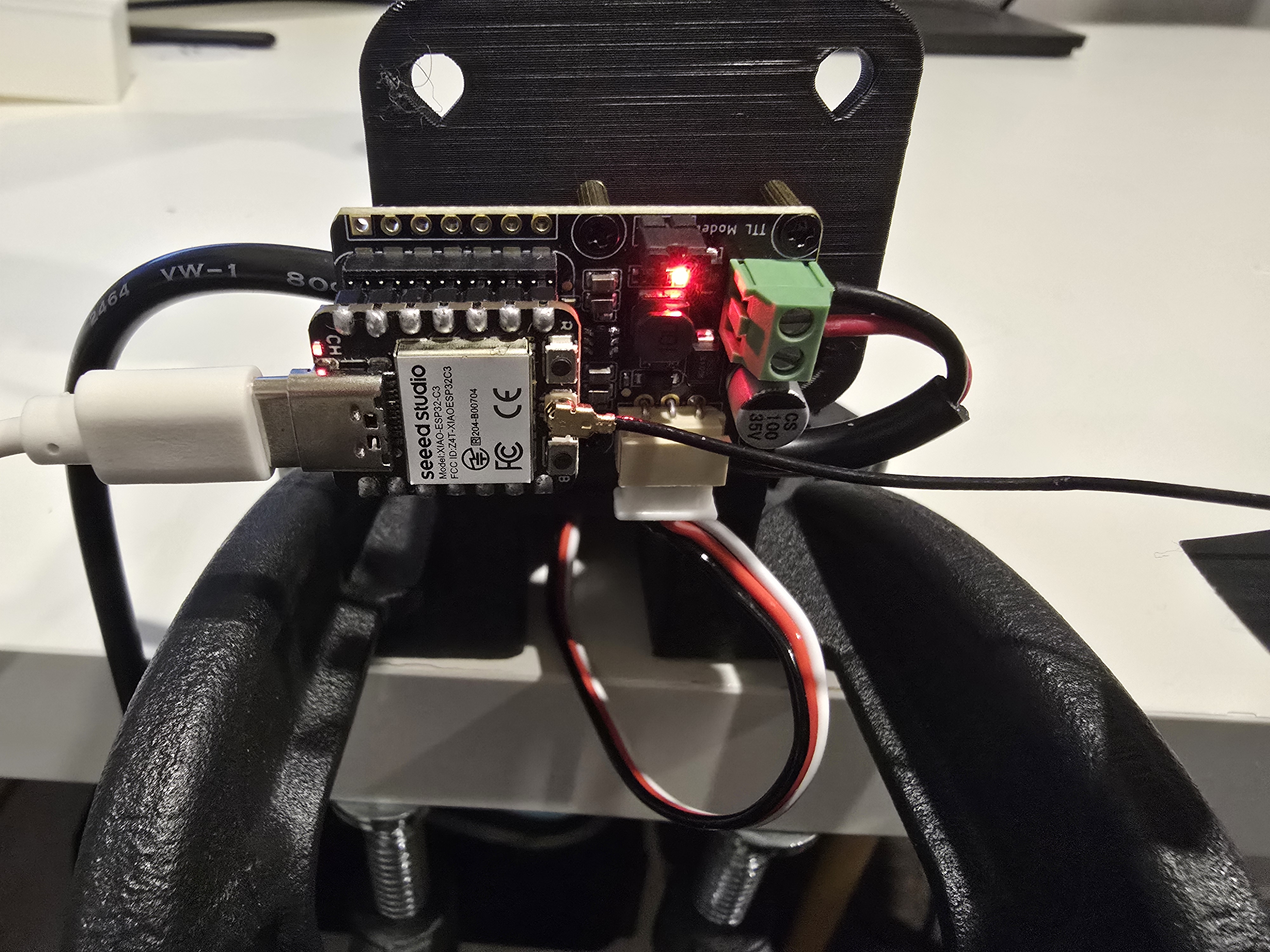
The LeRobot Follower arm is subscribed to an IoT Topic that is being published in real-time by the LeRobot Leader arm over AWS IoT Core, using a Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32C3 integrated with a Seeed Studio Bus Servo Driver Board, the driver board is controlling the 6 Feetech 3215 Servos over the UART protocol.
In this video I demonstrate how to control a set of Hugging Face SO-101 arms over AWS IoT Core, without the use of the LeRobot framework, nor using a device such as a Mac nor a device like Nvidia Jetson Orin Nano Super Developer Kit. Only using Seeed Studio XIAO ESP32C3 and AWS IoT.
You can find the source code for this solution here: https://github.com/chiwaichan/aws-iot-core-lerobot-so101
Good times
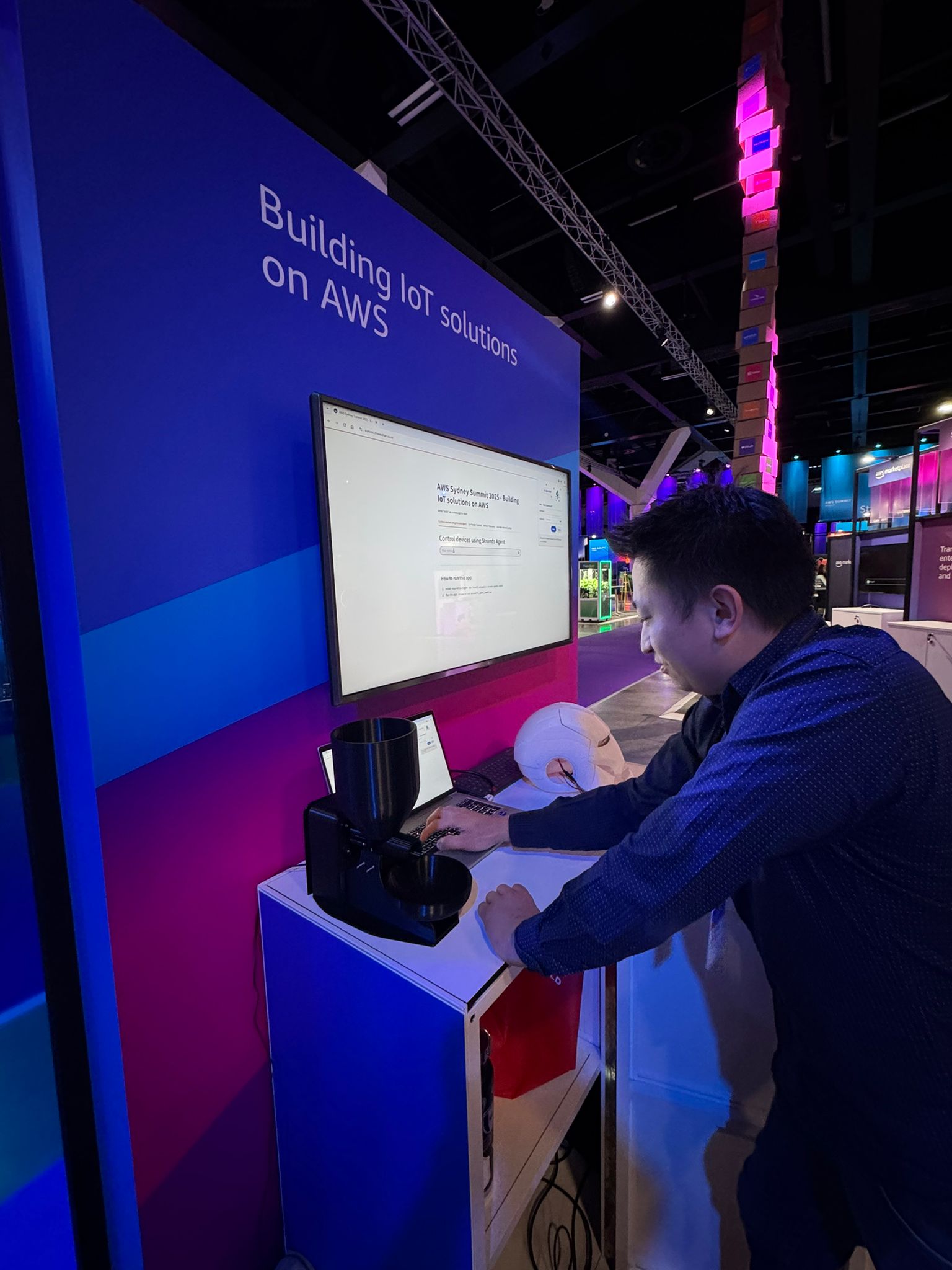


I was hungry and tried to feed myself but I forgot to bring cat food.
Here is the source-code Streamlit App I demoed at the AWS Sydney Summit, to demonstrate how to control IoT devices using the Strands Agents: https://github.com/chiwaichan/AWSSydneySummit2025Demo