Real-Time Voice Chat with Amazon Nova Sonic using React and AWS Amplify Gen 2
These days I am often creating small generic re-usable building blocks that I can pontentially use across new or existing projects, in this blog I talk about the architecture for a LLM based voice chatbot in a web browser built entirely as a serverless based solution.
The key component of this solution is using Amazon Nova 2 Sonic, a speech-to-speech foundation model that can understand spoken audio directly and generate voice responses - all through a single bidirectional stream from the browser directly to Amazon Bedrock, with no backend servers required - no EC2 instances and no Containers.
Goals
- Enable real-time voice-to-voice conversations with AI using Amazon Nova 2 Sonic
- Direct browser-to-Bedrock communication using bidirectional streaming - no Lambda functions or API Gateway required
- Use AWS Amplify Gen 2 for infrastructure-as-code backend definition in TypeScript
- Implement secure authentication using Cognito User Pool and Identity Pool for temporary AWS credentials
- Handle real-time audio capture, processing, and playback entirely in the browser
- Must be a completely serverless solution with automatic scaling
- Support click-to-talk interaction model for intuitive user experience
- Display live transcripts of both user speech and AI responses
Architecture
End-to-End Voice Chat Flow
This diagram illustrates the complete flow from a user speaking into their microphone to hearing the AI assistant's voice response.
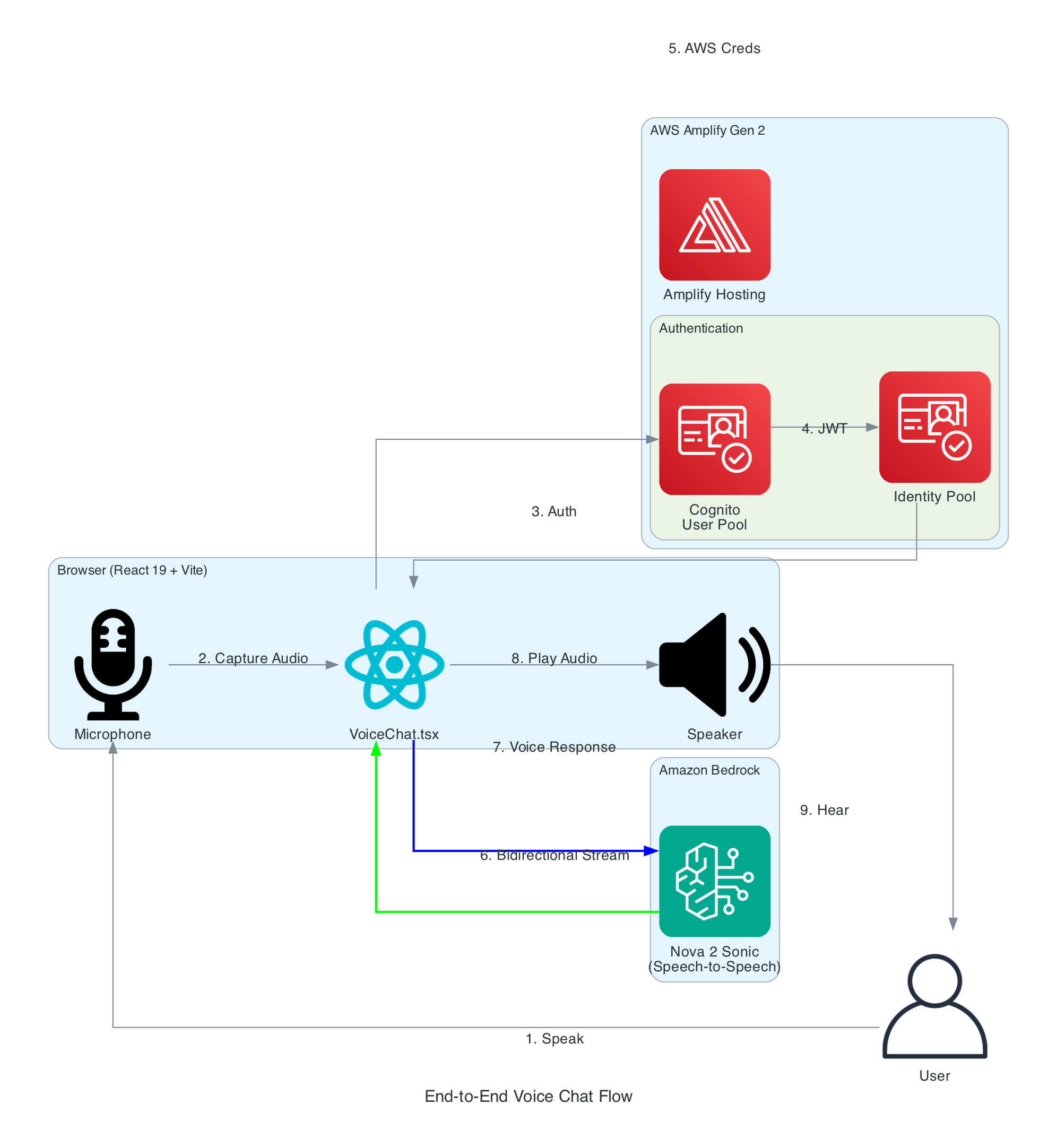
Flow Steps:
- User Speaks - User clicks the microphone button and speaks naturally
- Audio Capture - Browser captures audio via Web Audio API at 48kHz
- Authentication - React app authenticates with Cognito User Pool
- Token Exchange - JWT tokens exchanged for Identity Pool credentials
- AWS Credentials - Temporary AWS credentials (access key, secret, session token) returned
- Bidirectional Stream - Audio streamed to Bedrock via
InvokeModelWithBidirectionalStream - Voice Response - Nova Sonic processes speech and returns synthesized voice response
- Audio Playback - Response audio decoded and played through speakers
- User Hears - User hears the AI assistant's natural voice response
Interactive Sequence Diagram
Voice Chat Sequence Flow
From user speech to AI voice response via Amazon Nova 2 Sonic
React Hooks Architecture
This diagram details the internal architecture of the React application, showing how custom hooks orchestrate audio capture, Bedrock communication, and playback.
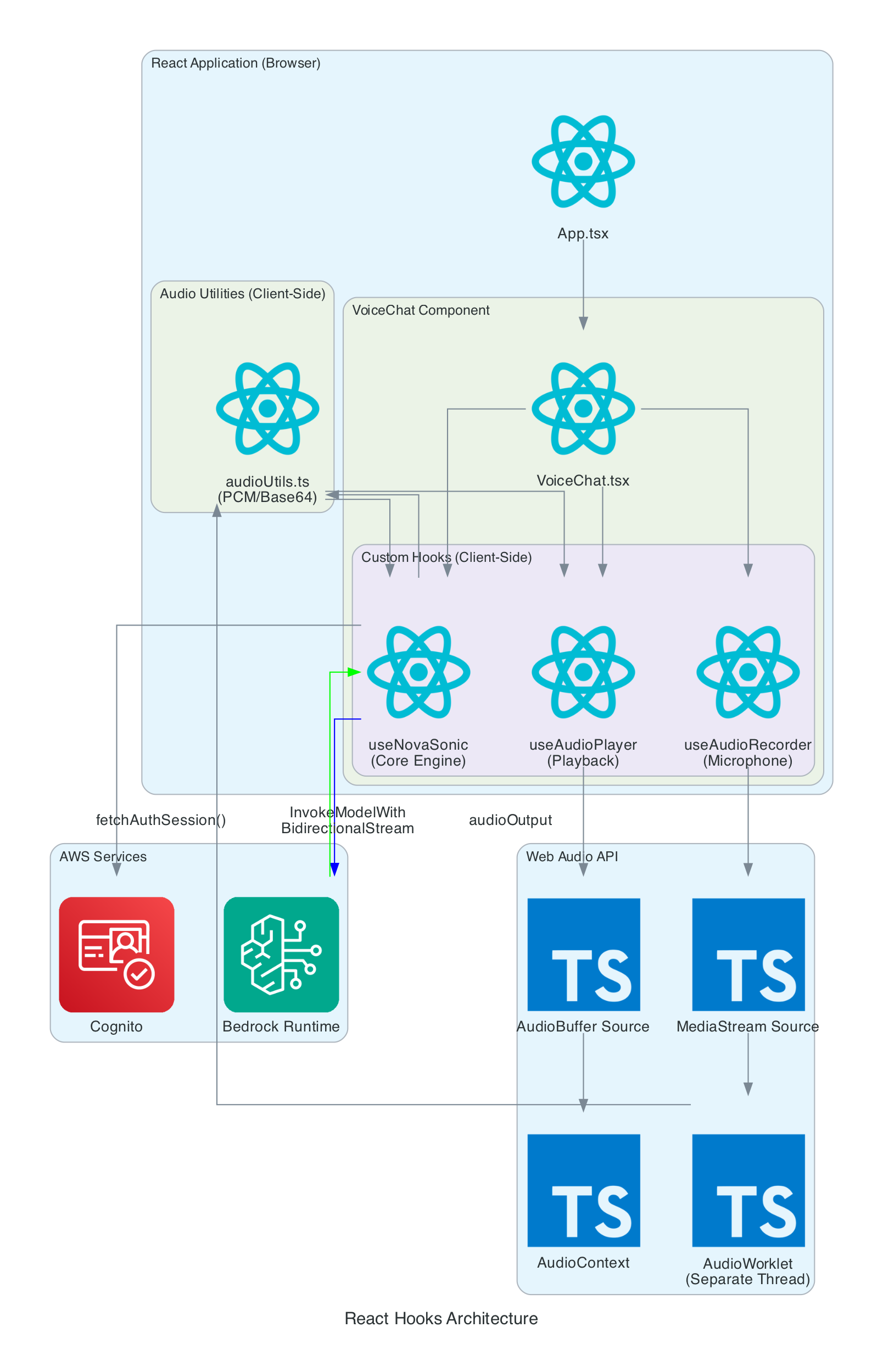
Components:
- VoiceChat.tsx - Main UI component that coordinates all hooks and renders the interface
- useNovaSonic - Core hook managing Bedrock bidirectional stream, authentication, and event protocol
- useAudioRecorder - Captures microphone input using AudioWorklet in a separate thread
- useAudioPlayer - Manages audio playback queue and Web Audio API buffer sources
- audioUtils.ts - Low-level utilities for PCM conversion, resampling, and Base64 encoding
Data Flow:
- Microphone audio captured by
useAudioRecordervia MediaStream - AudioWorklet processes samples in real-time (separate thread)
- Audio resampled from 48kHz to 16kHz, converted to PCM16, then Base64
useNovaSonicstreams audio chunks to Bedrock- Response audio received as Base64, decoded to PCM, converted to Float32
useAudioPlayerqueues AudioBuffers and plays through AudioContext
Authentication Flow
This diagram shows the multi-layer authentication flow that enables secure browser-to-Bedrock communication without exposing long-term credentials.
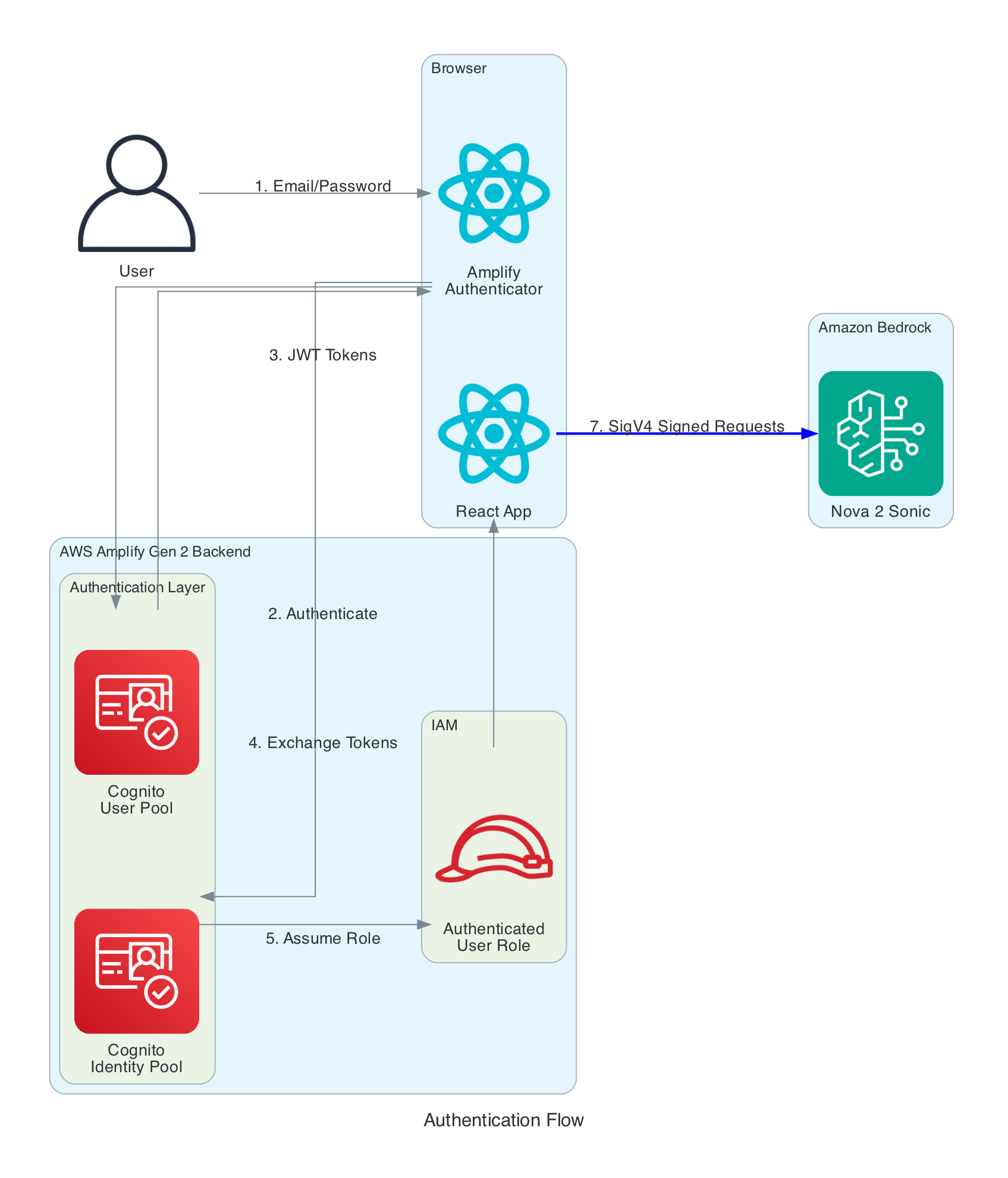
Authentication Layers:
- Cognito User Pool - Handles user registration and login with email/password
- Cognito Identity Pool - Exchanges JWT tokens for temporary AWS credentials
- IAM Role - Defines permissions for authenticated users (Bedrock invoke access)
- SigV4 Signing - AWS SDK automatically signs all Bedrock requests
Key Security Features:
- No AWS credentials stored in browser - only temporary session credentials
- Credentials automatically refreshed by Amplify SDK before expiration
- IAM policy scoped to specific Bedrock model (
amazon.nova-2-sonic-v1:0) - All communication over HTTPS with TLS 1.2+
Audio Processing Pipeline
This diagram shows the real-time audio processing that converts browser audio to Bedrock's required format and vice versa.
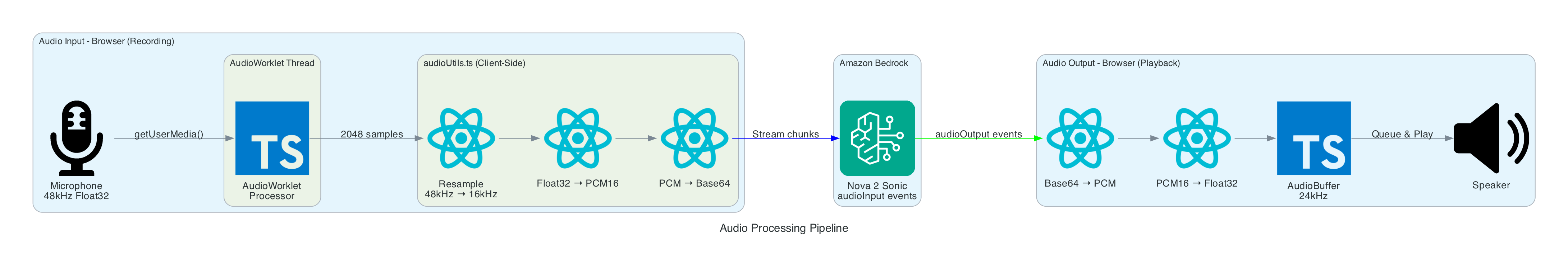
Input Processing (Recording):
- Microphone - Browser captures audio at native sample rate (typically 48kHz)
- AudioWorklet - Processes audio in separate thread, accumulates 2048 samples
- Resample - Linear interpolation converts 48kHz → 16kHz (Nova Sonic requirement)
- Float32 → PCM16 - Converts floating point [-1,1] to 16-bit signed integers
- Base64 Encode - Binary PCM encoded for JSON transmission
Output Processing (Playback):
- Base64 Decode - Received audio converted from Base64 to binary
- PCM16 → Float32 - 16-bit integers converted to floating point
- AudioBuffer - Web Audio API buffer created at 24kHz (Nova Sonic output rate)
- Queue & Play - Buffers queued and played sequentially through speakers
Interactive Sequence Diagram
Audio Processing Pipeline
Real-time audio capture, format conversion, and playback
Bidirectional Streaming Protocol
This diagram illustrates how the useNovaSonic hook manages the complex bidirectional streaming protocol with Amazon Bedrock.

Event Protocol: Nova Sonic uses an event-based protocol where each interaction consists of named sessions, prompts, and content blocks.
Input Events (sent to Bedrock):
- sessionStart - Initializes session with inference parameters (maxTokens: 1024, topP: 0.9, temperature: 0.7)
- promptStart - Defines output audio format (24kHz, LPCM, voice "matthew")
- contentStart - Marks beginning of content blocks (TEXT for system prompt, AUDIO for user speech)
- textInput - Sends system prompt text content
- audioInput - Streams user audio chunks as Base64-encoded 16kHz PCM
- contentEnd - Marks end of content block
- promptEnd / sessionEnd - Terminates prompt and session
Output Events (received from Bedrock):
- contentStart - Marks role transitions (USER for ASR, ASSISTANT for response)
- textOutput - Returns transcribed user speech and generated AI response text
- audioOutput - Returns synthesized voice response as Base64-encoded 24kHz PCM
- contentEnd - Marks end of response content
Async Generator Pattern:
The SDK requires input as AsyncIterable<Uint8Array>. The hook implements this using:
- Event Queue - Pre-queued initialization events before stream starts
- Promise Resolver - Backpressure control for yielding events on demand
- pushEvent() - Adds new events during conversation (audio chunks)
Serverless Architecture Overview
This diagram provides a comprehensive view of all components - the entire solution is serverless with no EC2 instances or containers to manage.
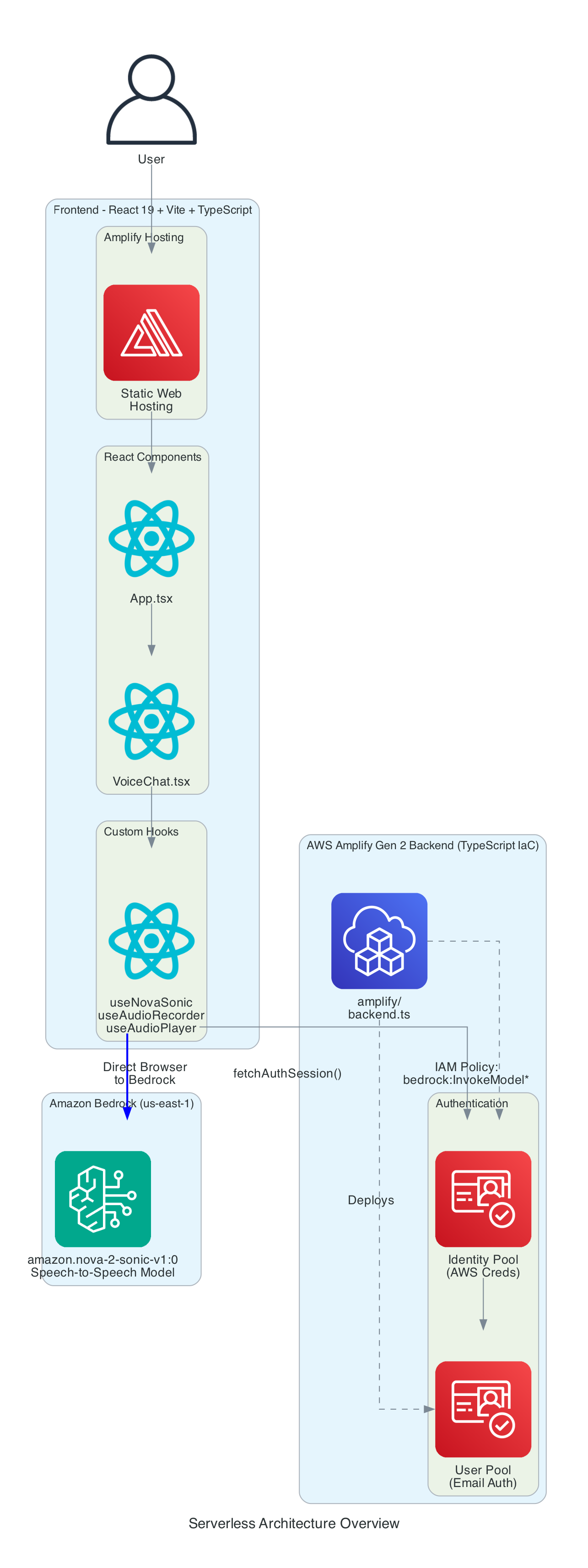
Frontend Stack:
- React - Component-based UI framework
- Vite - Build tool and dev server
- TypeScript - Type-safe development
- AWS Amplify Hosting - Static web hosting with global CDN
Backend Stack (Amplify Gen 2):
- amplify/backend.ts - Infrastructure defined in TypeScript
- Cognito User Pool - Email-based authentication
- Cognito Identity Pool - AWS credential vending
- IAM Policy - Grants
bedrock:InvokeModelpermission for bidirectional streaming
AI Service:
- Amazon Bedrock - Managed foundation model inference
- Nova 2 Sonic - Speech-to-speech model (us-east-1)
- Bidirectional Streaming - Real-time duplex communication
Technical Challenges & Solutions
Challenge 1: AudioWorklet CORS Issues
Problem: Loading AudioWorklet from external file fails with CORS errors on some deployments.
Solution: Inline the AudioWorklet code as a Blob URL:
const blob = new Blob([audioWorkletCode], { type: 'application/javascript' });
const workletUrl = URL.createObjectURL(blob);
await audioContext.audioWorklet.addModule(workletUrl);
URL.revokeObjectURL(workletUrl);
Challenge 2: Sample Rate Mismatch
Problem: Browsers capture audio at 48kHz, but Nova Sonic requires 16kHz input.
Solution: Linear interpolation resampling in real-time:
const resampleAudio = (audioData: Float32Array, sourceSampleRate: number, targetSampleRate: number) => {
const ratio = sourceSampleRate / targetSampleRate;
const newLength = Math.floor(audioData.length / ratio);
const result = new Float32Array(newLength);
for (let i = 0; i < newLength; i++) {
const srcIndex = i * ratio;
const floor = Math.floor(srcIndex);
const ceil = Math.min(floor + 1, audioData.length - 1);
const t = srcIndex - floor;
result[i] = audioData[floor] * (1 - t) + audioData[ceil] * t;
}
return result;
};
Challenge 3: SDK Bidirectional Stream Input
Problem: AWS SDK requires input as AsyncIterable<Uint8Array>, but events need to be pushed dynamically during the conversation.
Solution: Async generator with event queue and promise-based backpressure:
async function* createInputStream() {
while (isActiveRef.current && !ctrl.closed) {
while (ctrl.eventQueue.length > 0) {
yield ctrl.eventQueue.shift();
}
const nextEvent = await new Promise(resolve => {
ctrl.resolver = resolve;
});
if (nextEvent === null) break;
yield nextEvent;
}
}
Getting Started
GitHub Repository: https://github.com/chiwaichan/amplify-react-amazon-nova-2-sonic-voice-chat
Prerequisites
- Node.js 18+
- AWS Account with Bedrock access enabled
- AWS CLI configured with credentials
Deployment Steps
-
Enable Nova 2 Sonic in Bedrock Console (us-east-1 region)
-
Clone and Install:
git clone https://github.com/chiwaichan/amplify-react-amazon-nova-2-sonic-voice-chat.git
cd amplify-react-amazon-nova-2-sonic-voice-chat
npm install
- Start Amplify Sandbox:
npx ampx sandbox
- Run Development Server:
npm run dev
- Open Application:
Navigate to
http://localhost:5173, create an account, and start talking!
Summary
This architecture provides a reusable building block for voice-enabled AI applications:
- Zero backend servers - Direct browser-to-Bedrock communication
- Real-time streaming - HTTP/2 bidirectional streaming for low latency
- Secure authentication - Cognito User Pool + Identity Pool + IAM policies
- Audio processing pipeline - Web Audio API, AudioWorklet, PCM conversion
- Infrastructure as code - AWS Amplify Gen 2 with TypeScript backend definition
The entire interaction happens in real-time: speak naturally, and hear the AI respond within seconds.
